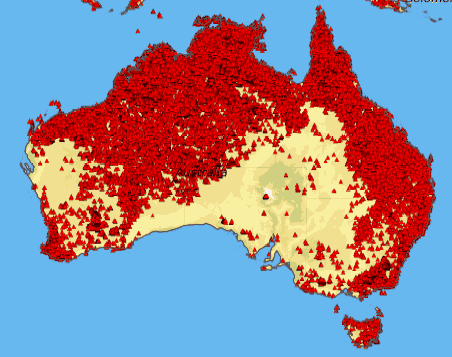
Image courtesy of MODIS Rapid Response System at NASA/GSFC
https://earthdata.nasa.gov/earth-observation-data/near-real- time/rapid-response
This composite satellite map shows where bushfires had occurred during the years 1997 to 2008.
The red markers is the area of Australia burnt between 1997 and 2008
About 115,000 and 230,000 fires per year were depicted by satellite remote sensing during the fire seasons 1998-1999 and 1999-2000 (14)
| Victoria | New South Wales | Australian Capital Territory |
| South Australia | West Australia | Queensland |
| Tasmania | Bushfire loss | Northern Territory |
Summary of major Bushfires in Australia
Australia is widely regarded as the most fire-prone country in the world.(1)
The composite satellite map above shows where bushfires had occured during the years 1997 to 2008.
The red markers is the area of Australia burnt between 1997 and 2008.
Bushfires have been part of the Australian environment since before human settlement of the continent. Some Australian flora and fauna has evolved to coexist with bushfires, and in the case of eucalypt forest, fire forms an integral part of its regeneration cycle. Aboriginal arrival to Australia resulted in an increased frequency in the incidence of bushfires, a pattern which was replicated upon European settlement (2).
The areas which experience the most severe bushfires usually occur in the south-eastern corner of Australia, south of a line from Sydney to Adelaide. This is because the most severe fire weather (hot, dry, strong winds) generally occurs in this part of the country. In association with this climatic influence, the south eastern areas of mainland Australia, Tasmania, and the south western corner of Western Australia also produce the tallest forests and heavy fuel loads. When these usually wet forests dry out the heavy fuel loads produce the most intense and devastating bushfires (Year Book Australia 1995 (1301.0)).

"Bushfires are a natural part of ecosystem processes in Australia. However, as human settlements expand into or adjacent to bushland areas, the risk to lives and property increases." Source: The Australian Journal of Emergency Management, Vol. 22 No. 2, May 2007
Bushfires caused significant damage during the 19th and 21st centuries.
Vast areas of grassland and forest have been burnt, large numbers of livestock were killed, houses and other buildings were destroyed and many human lives were taken.
Victoria.
The 'Black Thursday' fires of 6 February 1851 in Victoria, burnt the largest area (approximately 5 million ha) in European-recorded history and killed more than one million sheep and thousands of
cattle as well as taking the lives of 12 people.(3)
On 'Red Tuesday', 1 February 1898 in Victoria 260,000 ha were burnt, 12 people were killed and 2000 buildings were destroyed.(4) .
Between December 1938 to January 1939, 1.5-2.0 million ha were burnt, 71 people were killed and over 1000 homes destroyed in Victoria.(5). The most devastation occurred on 'Black Friday', 13 January 1939, when strong northerly winds intensified fires burning in almost every part of
the state. Townships were destroyed and others badly damaged. So much ash and smoke was generated that ash fell as far away as New Zealand.(6).
Five years later in 1944, bushfires in Victoria burnt an estimated one million ha, killed approximately 20 people and destroyed more than 500 houses.(7).
The 'Ash Wednesday' fires of 16 February 1983 caused severe damage in Victoria and South Australia. In Victoria, 210,000 ha were burnt, 2,080 houses destroyed, more than 27,000 stock lost and 47
people lost their lives . Property-related damage was estimated at over $200m and more than 16,000 fire fighters, 1,000 police and 500 defence personnel fought the fires
in Victoria. In South Australia, 208,000 ha were burnt, 383 houses were destroyed, 28 people were killed and property-related damage was estimated to be more than $200m .(8)
Eighty seven fires were started by lightning in the north east of Victoria on 8 January 2003. Eight of these fires were unable to be contained and joined together to form the largest fire in Victoria
since the 1851 "Black Thursday" bushfires. Burning for 59 days before being contained, the fires burnt over 1.3 million hectares, 41 homes and over 9,000 livestock, with thousands of kilometres of
fencing also being destroyed. Areas affected include Mt Buffalo, Bright, Dinner Plain, Benambra and Omeo.(9)
173 people perished in the Victorian bushfire inferno " Black Saturday " on the 7 th of February. 2009 which, destroyed 2,029 homes, 2,498 buildings, 59 Commercial Premises and the loss of 5,223
stock. It burnt out 411,239 hectares of land. (10)
New South Wales.
Serious bushfires occurred in New South Wales, in 1951-52, 1968-69,
1984-85 and 1993-94, in 1968-69 over one million ha were burnt and three people were killed.(11).
In 1984-85, 3.5 million ha were burnt, four lives were lost, 40,000 livestock were killed and $40m damage to property was caused.
In 1993-94, bushfires burnt 800,000 ha, destroyed 287 residential properties and other premises and killed four people. At the height of the 1993-94 fires, over
20,000 firefighters were deployed.(12).
Queensland.
Whilst bushfires in South-East Queensland have seldom been as severe as the worst fires that have occurred in the southern states, (such as the ‘Black Saturday’ fires that claimed 173
lives in Victoria in 2009,) serious fires have occurred in the region during most months of the year.
Contrary to the widely held belief, bushfires do destroy property(including urban property) and they do kill people in South- East Queensland.(13)
There were 2,618 fires in Queensland from July 2002 until June 2003 covering over one million ha.
The largest fire burnt an area of 200,000 ha.(14)
Tasmania.
Tasmania suffered their worst bushfires on 'Black Tuesday' 7 February 1967 when 110 fires that were within a 40 kilometre radius of Hobart converged during a seven-hour period, fanned by extreme
weather conditions.
Approximately 264,000 ha were burnt, 1,700 houses destroyed and 61 people were killed (Year Book Australia 1995 (1301.0).
Western Australia.
Western Australia experienced serious bushfires during 1960-61 when 359,000 ha were burnt.(15).
Northern Territory.
The Northern Territory experiences fires annually on a scale which dwarfs those in southern Australia. For example, in 1974-75, following lush vegetation growth due to heavy rainfall in the previous
two years, over 117 million ha or 15% of the total land area of the continent was burnt in central Australia during the fire season (Year Book Australia 1995 (1301.0). Extensive fires occurred in
the Northern Territory in the 1920s, 50s and mid-70s. A number of the fires were caused by lightning strikes associated with seasonal change (16). These
fires are part of the natural cycle and also a tradition in Aboriginal people of the region. Up to 50% of the northern Australian landscape is burnt each year, and most areas are burnt at least once
in every three years.(17)
When considering fire statistics, fires with larger areas do not necessarily translate into more serious impacts on human settlements. For example, of all the fires that occurred during January 1994
in New South Wales, one of the most damaging was one of the smallest, burning just 476 ha but destroying 101 houses. This was more than half of the total houses lost in New South Wales during that
bushfire emergency period.
Source: EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AUSTRALIA, http://www.ema.gov.au/ Accessed 14th May 2009
![]() Read : Historical Newspaper articles about Black Thursday
1851
Read : Historical Newspaper articles about Black Thursday
1851
Australia Wide Bushfires 1851 - 2009
During this period there were 815 Human fatalities and 9,946 people were injured. These Fires had affected 1,311,050 people and made 31,942 homeless. The Total estimated
Cost $1,673,697,366. Note this does not include the 7th of February 2009 fire loss, which has yet to be assessed.
Australia Wide Floods since 1790
There were over 2,300 recorded Human fatalities.(1a)
Australia Wide Tropical cyclones since 1839
There were over 2,100 recorded Human fatalities.(1a)
Australia Wide Severe storms since 1824
There were over 770 recorded Human fatalities.(1a)
Deaths from wildfire/bushfire disasters worldwide
| Year | Location | Deaths |
| 1871 | Peshtigo, Wisconsin, USA (18) | 1200 |
| 1918 | Cloquet, Minnesota, USA (19) | 453 |
| 1894 | Hinckley, Minnesota, USA (20) | 418 |
| 1881 | Thumb region, Michigan, USA (21) | ~300 |
| 1916 | Matheson, Ontario, Canada (22) | 282 |
| 1997 | Sumatra, Kalimantan, Indonesia (23) | 250 |
| 1987 | Greater Hinggan, China (24) | 213 |
| 2009 | Victoria, Australia | 173 |
Partially Referenced from:
EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AUSTRALIA, http://www.ema.gov.au/ Accessed 14th May 2009
Bushfire area burnt - Source: CFA website; DPI/DSE website; R.H. Luke and A.G. McArthur, Bushfires in Australia, AGPS, 1978; Reports of the 1939 and 1944 Royal Commissions; A.G. McArthur, N.P. Cheney
and J. Barber, The fires of 12 February 1977 in the Western District of Victoria, CSIRO and CFA, 1982; R. Murray and K. White,
(1) Reference. Blong, R (2005) ‘Natural hazards risk assessment - An Australian perspective’.
Issues in Risk Science 4, Benfield Hazard Research Centre, London, p. 28.
(1) Source. 1301.0 / 2008 / Yearbook Complete / Understanding natural hazard impacts on Australia.
(2) Source. Florence 1996
(3) Source. CFA 2003a; DSE 2003b
(4) Source. Foley 1947
(5) Source. DSE 2003b, 2003c
(6) Source. DSE 2003c.
(7) Source. DSE 2003b
(8) Source. DSE 2003d
(9) Source. Bush and Forest Fires in Australia www.fire.uni-freiburg.de/
(10) Source. Bush and Forest Fires in Australia www.fire.uni-freiburg.de/
(11) Source. Linacre and Hobbs 1977; RFS 2003a
(12) Source. RFS 2003a,Year Book Australia 1995 (1301.0
(13) Source. Bush and Forest Fires in Australia www.fire.uni-freiburg.de/
(14) Source. Blong, R (2005) ‘Natural hazards risk assessment - An Australian perspective’
(15) Source. Linacre and Hobbs 1977
(16) Source. Bushfires Council of the Northern Territory 2003
(17) Source. Anderson 1999
Source. Emergency Management Australia, Attorney-General’s Department. EMA disasters database. Events by category. http://www.ema. gov.au/ema/emadisasters.nsf (accessed 14th May
2009).
(1a) Reference. Blong, R (2005) ‘Natural hazards risk assessment - An Australian perspective’.
Issues in Risk Science 4, Benfield Hazard Research Centre, London, p. 28.
(1a) Source. 1301.0 / 2008 / Yearbook Complete / Understanding natural hazard impacts on Australia.
Reference:
Note the fire in 1949 Landes region, France the death toll was 80.
Source: Forestry 1977 50(1):89-91; doi:10.1093/forestry/50.1.89 © 1977 by Institute of Chartered Foresters.
The 1825 Miramichi, New Brunswick, Canada fires MIRAMICHI."---The following account of the loss and Lives and Property sustained by the late conflagration at Miramichi, is extracted from an abstract
published there, by order of the "Committee appointed for the relief of the sufferers." Persons burnt, 130; drowned, 10; deaths from injury received by the fire, 20---Total, 160."
http://www3.gendisasters.com/fires/4314/miramichi,-nb-fire,-oct-1825
(18) Source: 1871 Peshtigo, Wisconsin, USA http://www.peshtigofire.info/ Accessed: 14th July 2009
(19) Source: 1918 Cloquet, Minnesota, USA COMMEMORATING THE 80TH ANNIVERSARY OF THE FIRES OF 1918 by Lois E. Johnson President, Moose Lake Area Historical
Society http://www.mnhs.org Accessed: 14th July 2009
(20) Source: The Great Hinckley Fire of 1894 http://www.hinckley.govoffice2.com/ Accessed: 14th July 2009
(21) Source: 1881 Thumb region, Michigan, USA http://www.ns.umich.edu/htdocs/releases/story.php?id=1245
http://www.associatedcontent.com/article/28070/attractions_in_port_hope_michigan.html Accessed: 14th July 2009
(23) Source: 1997 Sumatra, Kalimantan, Indonesia Death toll: >250 human due to aircraft and maritime accidents associated with the fires. GFMC:
Bush and Forest Fires in Australia www.fire.uni-freiburg.de/GFMCnew/.../20050112_aus.htm www.fire.uni-freiburg.de/iffn/iffn_22/iffn22.pdf
Accessed: 14th July 2009
(22) Source: 1916 Matheson, Ontario, Canada. Natural Resources Canada.
www.nrcan.gc.ca Accessed: 14th July 2009
(24) Source: 1987 Greater Hinggan, China Global Fire Monitoring Center (GFMC)
http://www.fire.uni-freiburg.de/ http://www.fire.uni-freiburg.de/GFMCnew/2002/1002/20021002_cn.htm Accessed: 14th July 2009
