"...volcanic activity must be considered a serious environmental hazard and risk for the Australian mainland. " Source: The risk of volcanic eruption in mainland Australia - E. B. Joyce

A volcano filled with water. Erupted 4500 years ago
Mount Gambier.
The maar crater, with a 5km circumference, is now a volcanic lake, and is the
local township's water supply.
The depth of water and volume of Blue Lake are approximately 70 m and 36x106 m3 (36,000 ML)
respectively. The steep walls of the lake result in a surface catchment area (0.9x106 m2).
Why does the Lake change colour?
There were many theories about the famous colour change of the Lake, from grey in winter to vivid blue in summer
and the following summarises the general understanding from recent research.
The colour change happens over a few days in late November and early December and continues to deepen during
summer.
The clear water in Blue Lake turns vibrant blue in summer for two reasons.
First, the higher position of the sun in summer than in winter means more light hits the surface of the Lake.
This increases the blue light that is scattered back out from the Lake by small particles.
Pure water tends to scatter light in the blue range, small particles (such as CaCO3 or calcium carbonate
crystals) scatter light in the blue-green range and dissolved organic matter, (tannins) scatter in the
yellow-brown range.
Second, during spring the surface of the Lake warms, dissolved carbon dioxide is released into the air
as a gas, the pH increases and this water becomes over-saturated in calcite which begins to precipitate out.
Tiny calcite crystals form and as they fall down to the bottom of the Lake they capture organic material
“cleaning” this matter from the water.
Each year a new layer of calcite about 3mm thick and organic material 1mm thick settles on the bottom of the Lake.
It is generally accepted that there is an annual calcium precipitation cycle which has a role in clarifying the Lake around November, which precedes the colour change to blue.
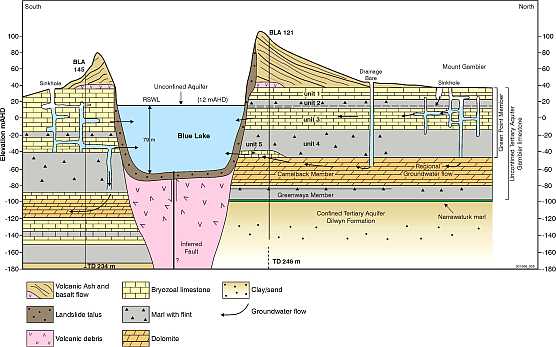
Image source courtesy:
Impact of Stormwater Recharge on Blue Lake, Mount Gambier's Drinking Water Supply Vanderzalm
Carbon Dioxide ( CO2 ).
" This change in water colour can be explained by the effect of CO2.
As CO2 degasses from the magma and migrates to surface it reacts with the Mount
Gambier Limestone. This reaction dramatically increases the concentration of calcium
dissolved in the water.
The change in temperature of the Ca-rich lake causes the calcium
to become supersaturated and precipitate out of solution.
Micro-crystallites of calcium carbonate refract the sunlight to the blue wavelength light
that is seen. "
Source: CO2CRC WA Dept. of Industry & Resources
Whistler Research
Scientific Marvels & Geosequestration
Analogues - Max Watson CO2CRC e News Agust 2004, Issue 01
Other Articles
Is there a risk of a volcanic eruption in Australia ?
Drought and Bushfires in Victoria 1851 Black Thursday
Chronoloy of Australian Major Bushfires
Chronoloy of Australian Major Droughts